Review of the Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Workbook for 13 Year Olds?

Every bit humans, we will never accept complete control over what we feel, but we have a lot more than influence over how we feel than you might have heard.
The skills that allow you lot to manage and direct your emotions are called emotion regulation skills (see cocky-regulation), and it doesn't take a pilgrimage to a holy site or thousands of dollars to larn these secrets to feeling better.
This article will see you learn about emotion regulation and help you lot develop and improve the skills necessary for staying balanced and emotionally stable.
Before you read on, we idea you might similar to download our three Emotional Intelligence Exercises for free. These scientific discipline-based exercises will non only enhance your ability to empathize and regulate your emotions but will likewise give you the tools to foster the emotional intelligence of your clients, students or employees.
An Explanation of Emotion Regulation in Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Emotion regulation is one of the 4 skills modules of Dialectical Behavior Therapy or DBT. These 4 modules include:
- Interpersonal effectiveness;
- Distress tolerance/reality acceptance skills;
- Emotion regulation;
- Mindfulness skills.
The emotion regulation portion focuses on skills that benefit everyone who has emotions (i.e., every human!), but they are most beneficial for those struggling with mood or personality disorders, especially those with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD).
In this module, clients larn how to sympathize and accept their emotions, reduce their emotional vulnerability and volatility, and decrease their emotional suffering (Bray, 2013).
One of the nigh important aspects of treatment is recognizing that negative or painful emotions are not inherently bad. Clients are encouraged to take that they will undoubtedly experience negative emotions in their life, no matter how happy or well-counterbalanced they may be.
Instead of focusing on avoiding or denying the presence of the negative, DBT clients larn valuable skills to keep their emotions in check and avert emotional dysregulation.
What Is Emotional Dysregulation?

If emotion regulation is the process of controlling i'southward emotions, keeping them in balance and away from extremes, then it's probably easy to effigy out what emotional dysregulation is—the disability to control one's emotional responses.
Emotional dysregulation is a process with three master steps:
- An internal or external effect (thinking virtually something deplorable or encountering someone who is aroused) provokes a subjective feel (emotion or feeling);
- And so a cognitive response (thought) is followed by an emotion-related physiological response (for example, an increase in heart charge per unit or hormonal secretion);
- The process culminates in a behavior (avoidance, physical action, or expression; PCH Treatment Center, n.d.).
People who are struggling with emotional dysregulation react to relatively mild negative events in an emotionally exaggerated mode; they may weep, scream, accuse, or blame those around them, or engage in passive-aggressive behaviors or other behaviors that tin can disrupt relationships and escalate disharmonize (PCH Handling Center, n.d.).
Recent research has proposed that emotional dysregulation, peculiarly when nowadays in those suffering from BPD, is made up of four components:
- Emotion sensitivity;
- Heightened and unstable mood or emotions;
- A lack of appropriate emotion regulation strategies;
- A plethora of maladaptive emotion regulation strategies (Carpenter & Trull, 2013).
DBT Self Help: 3 Emotion Regulation Questionnaires
At that place are a few different self-assessment tools available to learn about your own emotion regulation abilities. The three most popular and virtually evidence-backed scales are included beneath.
Emotion Regulation Questionnaire
The Emotion Regulation Questionnaire, or ERQ, is the most popular emotion regulation scale among psychology researchers. Information technology was developed in 2003 by James Gross and John Oliver, based on v studies spanning the question development, validity and reliability, and construction of the questionnaire.
The scale is composed of x items, rated on a scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly hold). The calibration covers two facets, the Cognitive Reappraisal facet and the Expressive Suppression facet, and produces a separate score for each facet.
The six items that brand upwards the Cognitive Reappraisal facet are as follows:
- When I want to feel more positive emotion (such as joy or amusement), I change what I'm thinking almost;
- When I want to feel less negative emotion (such every bit sadness or acrimony), I change what I'm thinking well-nigh;
- When I'm faced with a stressful situation, I make myself think nigh it in a way that helps me stay calm;
- When I want to feel more positive emotion, I modify the way I'chiliad thinking most the situation;
- I control my emotions by changing the way I think near the situation I'm in;
- When I desire to feel less negative emotion, I change the fashion I'g thinking nearly the situation.
The four items that make up the Expressive Suppression facet include;
- I go on my emotions to myself;
- When I am feeling positive emotions, I am careful non to express them;
- I control my emotions past not expressing them;
- When I am feeling negative emotions, I make sure non to express them.
For more than information on using this calibration, click hither.
Interpersonal Emotion Regulation Questionnaire
The Interpersonal Emotion Regulation Questionnaire, or IERQ, was developed to focus on the less attended interpersonal emotion regulation processes, rather than interpersonal processes. This scale was adult very recently (2016) by researchers Hofmann, Carpenter, and Curtiss.
It consists of 20 items and covers four factors, each containing 5 items rated on a scale from 1 (not true for me at all) to 5 (extremely true for me).
The iv factors and their associated items are every bit follows:
- Enhancing Positive Affect:
o I like being effectually others when I'm excited to share my joy;
o Being in the presence of certain other people feels good when I'one thousand elated;
o I similar beingness in the presence of others when I feel positive because it magnifies the good feeling;
o Because happiness is contagious, I seek out other people when I'grand happy;
o When I feel elated, I seek out other people to make them happy. - Perspective Taking:
o Information technology helps me deal with my depressed mood when others point out that things aren't every bit bad as they seem;
o Having people remind me that others are worse off helps me when I'm upset;
o When I am upset, others make me feel amend by making me realize that things could be a lot worse;
o When I am annoyed, others tin can soothe me past telling me non to worry;
o Having people telling me non to worry can calm me down when I am anxious. - Soothing:
o I look for other people to offer me compassion when I'm upset;
o Feeling upset often causes me to seek out others who will express sympathy;
o I look to others for comfort when I feel upset;
o I look to other people when I experience depressed merely to know that I am loved;
o When I feel sad, I seek out others for consolation. - Social Modeling:
o It makes me experience better to learn how others dealt with their emotions;
o Hearing another person'south thoughts on how to handle things helps me when I am worried;
o Seeing how others would handle the same situation helps me when I am frustrated;
o When I'm distressing, it helps me to hear how others accept dealt with similar feelings;
o If I'one thousand upset, I like knowing what other people would practice if they were in my situation.
This calibration produces iv scores, one for each subscale, and they are calculated by simply adding upward the score for each particular. Each subscale has a minimum score of 5 and a maximum score of 25.
Click here to acquire more about the IERQ.
Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire
The Cerebral Emotion Regulation Questionnaire, or CERQ, is a scale for identifying the cognitive coping strategies used afterward a negative experience (Garnefski, Kraaij, & Spinhoven, 2001). It differs from other emotional regulation questionnaires in its focus on the individual's thoughts and exclusion of the behavior; it aims to find out what cognitive strategies the individual uses, rather than how they conduct.
The calibration is composed of 36 items rated on a scale from 1 ([nigh] never) to 5 ([almost] always). Information technology includes ix split up cognitive coping strategies, with iv items comprising each strategy.
The ix strategies and an example detail are included below:
- Cocky-blame – I experience that I am the one who is responsible for what has happened;
- Acceptance – I call back that I have to accept that this has happened;
- Rumination – I want to understand why I feel the style I do nigh what I have experienced;
- Positive Refocusing – I recollect of pleasant things that have nothing to do with information technology;
- Refocus on Planning – I recall about how I can best cope with the state of affairs;
- Positive Reappraisal – I think that I can get a stronger person as a issue of what has happened;
- Putting into Perspective – I think that it hasn't been too bad compared to other things;
- Catastrophizing – I frequently think that what I accept experienced is much worse than what others have experienced;
- Other-blame – I think about the mistakes others have made in this affair.
To learn more nigh how this calibration is used in research, click here.
10 DBT Emotion Regulation Strategies & Techniques
 One of the best things about DBT is its focus on practical, real-earth skills and techniques.
One of the best things about DBT is its focus on practical, real-earth skills and techniques.
In this form of therapy, you won't have to worry about vague ideas surrounding healing and moving frontwards; your therapist volition take a detailed listing of skills, strategies, and techniques you lot can use to start feeling and doing better.
Practicing Real-World Skills. Free Image Courtesy of Pixaby.
A few of the best strategies and techniques are discussed below.
Understanding and Labelling Emotions
One of the virtually powerful tools in emotion regulation is simply identifying and naming the emotion you are feeling.
DBT encourages clients to use descriptive labels for their feelings rather than vague or general terms. The thought behind this skill is that to manage an emotion, yous must first know what it is.
Clients of DBT will also acquire about the deviation betwixt main and secondary emotions, and how to address each in the virtually helpful style.
Primary emotions: the initial reaction to an outcome or to triggers in your surroundings.
Secondary emotions: the reaction to your chief emotions or thoughts (Bray, 2013).
Main emotions are often completely natural reactions to things effectually usa, like being sad when a loved ane dies, or angry when someone is rude to us. However, secondary emotions are more unsafe and more than inside our command; nosotros generally have more of a choice about how to reply to the fact that nosotros are pitiful when someone dies.
Secondary emotions can push us towards behaviors that are destructive and maladaptive, making it essential to acquire how to accept your primary emotion without judging yourself for feeling it.
In DBT sessions, you may also discuss myths surrounding emotions, such as the idea that there is a "correct" and a "wrong" way to feel about certain events or situations. Our emotions are unique, organic experiences that cannot be molded to fit ideas of what is "normal," and to endeavor tin be harmful.
In fact, emotions are adaptive evolutionary traits—they developed because they helped us function better, both by helping united states communicate with others and by alerting u.s.a. to things in our environment that are beneficial or potentially problematic (Bray, 2013).
Learning to better understand, recognize, and label emotions is an enormously helpful skill to have, and not only will it give yous a good foundation for managing your emotions, simply information technology volition also help you empathise and understand with others.
Mindfulness
Mindfulness tin exist described every bit living your life in the present instead of existence stuck in the past or the time to come (Tartakovsky, 2015). Practicing mindfulness helps us get more aware of our thought patterns, our emotions, and how our thoughts and feelings affect our reactions to events.
At that place are two categories of mindfulness skills: "What" skills and "How" skills:
- "What" skills:
o Find;
o Describe;
o Participate. - "How" skills:
o Not-judgmentally;
o Ane-mindfully;
o Effectively (Dietz, 2012).
If yous're interested in learning more than most how to practice mindfulness, bank check out our postal service on mindfulness exercises and techniques here.
Letting Go of Painful Emotions
 Maybe the most important emotion regulation skill, learning to let get can be very difficult merely is worth the effort you lot invest.
Maybe the most important emotion regulation skill, learning to let get can be very difficult merely is worth the effort you lot invest.
Humans have a tendency to go stuck when attempting to procedure negative emotions. Instead of merely letting them go, we often concur always tighter to them, obsessing over every little bit of our emotional experience and wondering why it'southward happening to us.
Acknowledging Hard Emotions. Image past Pexels from Pixaby.
It sounds paradoxical, just the act of accepting that we are feeling emotions we would rather not feel can be the fundamental to letting go of them. When we take that we are suffering, we stop running from the difficult emotions and plough to face them—and when we do, we might see that it wasn't the big bad monster we thought it was, but a smaller and more manageable beast.
Follow these steps to work on your power to let become of negative emotions:
- Observe your emotion. Acknowledge that it exists, stand up back from it, and get yourself unstuck from it;
- Try to experience your emotion as a wave, coming and going. You lot may notice it helpful to concentrate on some part of the emotion, like how your body is feeling or some image about it. For example, you could use this imagery:
"Try to imagine an bounding main wave flowing through you, only not so big that it knocks you over. Don't try to push the emotion away. This makes it bigger and increases our suffering. Don't refuse the emotion. Don't estimate your emotion. Information technology is not practiced or bad. It is just there. There are no bad emotions, just emotions. Acrimony, fear, sadness are all painful emotions, merely they are groovy. Anybody has them, and they are just as valid every bit the happy emotions. At the same fourth dimension, do not hang on to your emotion. Don't rehearse it over and over to yourself. Don't escalate it or make information technology bigger. Sometimes when we experience a very painful emotion, like acrimony or a deep grief, we agree on to it, or we intensify information technology, making it stronger and stronger, in our efforts to deal with it or to give information technology our full attending. Try not to practice this. Merely let it be however information technology is. This tin can outcome in a lessening of the pain."
- Recognize that you are not your emotion. Your emotion is role of you, but it is not all of you lot. You are more than your emotion;
- Practise not necessarily human activity on the emotion; having the emotion does not hateful that you have to human action. You may just need to sit with the emotion. Often, acting can intensify and prolong the emotion;
- Practice LOVING your emotions. This tin can be a difficult concept. Why would we want to love painful emotions?
We tin learn to love our emotions merely the way we can learn to love (accept) anything else most ourselves or our experience that nosotros cannot alter—our age, our meridian, freckles, the birds that sing early in the morning and wake us up, the atmospheric condition, the size of our feet, allergies, etc.
Remember that acceptance (dear) and approval are two unlike things. You don't have to like your freckles, only they are there and you can't change that, so if yous merely take or love them, you lot will feel a lot better than if you lot keep fighting the thought that they are there (Dietz, 2012).
Emotion Regulation Tips for the Holidays
With the holidays coming up, you might be visiting with family unit you lot don't see in everyday life. These go-togethers tin be peachy opportunities to reconnect with loved ones, only they can also be stressful and emotionally charged.
Follow these DBT self-help tips to get through your holiday visits with dignity and grace (Dietz, 2012).
Take Care of Your Torso
To accept a salubrious mind, it's extremely helpful to offset with a good for you trunk. Take intendance of yourself by eating good for you meals, exercising regularly, getting enough slumber, avoiding toxic or mood-altering substances, and treating any illnesses or issues that require treatment.
We don't brand the best decisions when we are feeling sick, tired, or hungry, then eliminating these physical problems will make it easier for you lot to maintain your emotional remainder.
Increasing Positive Emotions
Focus on increasing your positive emotions during the holiday season. You shouldn't ignore your negative emotions, but make sure to leave room for the positive as well.
Find Means to Have Fun
This one is self-explanatory—give yourself permission and the opportunities to enjoy yourself during the holidays.
Work on Relationships
Holiday gatherings are a keen opportunity to repair and restart relationships with friends that you haven't seen in a while. Leave yourself open up to the possibility of renewing old friendships, as well equally to forging new friendships.
Peradventure most important of all, commit to maintaining and strengthening your current relationships with family, friends, and anyone else you are likely to see on your vacation travels.
Exist Present to and Mindful of the Positive
Focus on the good things that your holiday season has brought you, such as seeing an onetime friend, getting a present that you're really excited nigh, or attending a fun New Year's Eve political party. Even if bad things happen, there'due south bound to be at least i or two positive things to enjoy.
Be Unmindful of Worries
While y'all're focusing on the positive, it volition make the next suggestion easier to implement: putting your worries and insecurities aside. Oversupply out the negative in your caput with all the positive that y'all can find. Remind yourself that you deserve to have fun, to savor your time with friends, and to bask in the warmth of a loving family. Make room in your mind for the positive, and the negative will have less space to fill (Dietz, 2012).
STOPP
If y'all're struggling with controlling your emotions, consider how to STOPP (Vivyan, 2015).
STOPP is a strategy that will help you in the heat of the moment when yous are dealing with intense emotions. Information technology incorporates aspects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), DBT, and mindfulness meditation to help you lot more finer accost and manage your emotional response to a challenging, hard, or rage-inducing incident.
STOPP stands for:
- Southward – Stop!
o Merely pause for a moment. - T – Take a Breath
o Notice your animate as you lot breathe in and out. - O – Discover
o What thoughts are going through your mind right now?
o Where is your focus of attention?
o What are you reacting to?
o What sensations do you detect in your trunk? - P – Pull Back – Put in Some Perspective
o What'southward the bigger movie?
o Take the helicopter view;
o What is another way of looking at this situation?
o What would a trusted friend say to me right now?
o Is this thought a fact or an opinion?
o What is a more than reasonable explanation?
o How of import is this? How important volition it be in 6 months' time? - P – Do What Works – Proceed
o What is the best affair to do right at present? For me? For others? For the situation?
o What tin can I practise that fits with my values?
o Do what will be effective and appropriate (Vivyan, 2015).
If you learn only one skill that volition help you to more effectively regulate your emotions, this should be the 1 you acquire. Learning how to pause in between an intense emotional reaction and your ensuing actions is one of the most valuable and life-changing skills that a person can accept. Practice STOPPing, and you will be in a keen position to manage your most hard emotions.
Differentiating Between Good for you and Unhealthy Emotion Regulation Activities
 In that location are many techniques to assistance you steer your emotions in the correct direction, or to maintain your positive mood and emotional residual.
In that location are many techniques to assistance you steer your emotions in the correct direction, or to maintain your positive mood and emotional residual.
There are likewise many techniques that on the surface seem similar they volition help you keep your emotional balance just upon further consideration reveal themselves to exist unhealthy.
Different activities might work best for you, but these lists are a good start if y'all are unsure where to brainstorm separating healthy from unhealthy activities.
Healthy activities that assistance y'all regulate your emotions include:
Writing as Cocky-Care. Image by David Schwarzenberg on Pixaby.
- Talking with friends;
- Exercising;
- Writing in a journal;
- Meditation;
- Therapy;
- Taking care of yourself when physically ill;
- Getting acceptable sleep;
- Paying attending to negative thoughts that occur before or after strong emotions;
- Noticing when you need a interruption—and taking it!
These activities are healthy because they not only contribute to improve management of your emotions, they do non cause yous any damage.
Unhealthy activities that may seem like they help, merely actually hurt, include:
- Abusing alcohol or other substances;
- Self-injury;
- Avoiding or withdrawing from hard situations;
- Physical or verbal assailment;
- Excessive social media apply, to the exclusion of other responsibilities (Rolston & Lloyd-Richardson, n.d.).
These activities tend to feel good and help in the moment, also equally provide a better strategy than "total avoidance" of situations that y'all inevitably will accept to face.
When you are tempted to engage in an unhealthy activity, consider an activity that builds a sense of achievement instead. Try an activity that will result in y'all learning something new or developing a new skill, and allow yourself the space to build on it every day.
Doing something positive and fulfilling like this tin not but increase your skills and boost your positive emotions merely will also go out less room for negative emotions (Rolston & Lloyd-Richardson, northward.d.).
8 Emotional Regulation Worksheets & Emotion Pictures
Aside from the strategies and techniques listed higher up, there are also several helpful handouts, worksheets, and even images that tin can aid you in developing your DBT skills and improving your emotion regulation.
Below are eight of the best worksheets, handouts, and emotion pictures bachelor.
Practicing Radical Acceptance
This worksheet helps you to identify and understand a situation or emotion you lot are struggling to accept.
First, y'all identify your context; "What is the challenge or state of affairs?"
Side by side, y'all describe the aspect of this situation that is difficult for you to accept.
Then you describe the reality of that situation.
After describing the reality, it asks you to remember nearly the antecedents – or causes – that came before that reality (hint: many of them you lot volition find to be outside of your command).
Next, yous practice radical acceptance with your whole beingness (mentally, physically, and spiritually), describing how yous accomplished this. The worksheet encourages you to endeavour the following:
"Inhale deeply, settle into an accepting, open up position. Become enlightened of your thoughts and emotions that struggle with your reality – then release them. Utilise credence techniques such every bit visualization, awareness exercises, or affirmations. Concentrate on a mantra of credence, such equally "That's just how it is," or "All is the way it should be.'"
Finally, yous charge per unit your power to handle the distress of this difficult situation both earlier and subsequently practicing radical acceptance, on a scale from 0 (you lot just tin can't take it) to 10 (total acceptance of reality).
Here'southward the free link to Practicing Radical Acceptance.
Interpersonal Effectiveness Skills
Interpersonal Skills Acronyms lists the DBT skills related to interpersonal effectiveness, including objective effectiveness, relationship effectiveness, and self-respect effectiveness, and also provides useful tips to put these skills into practice.
The department on objective effectiveness skills (DEAR MAN) outlines each skill and includes the post-obit tips for building and using them:
Describe
- Use articulate and concrete terms to draw what you lot want;
- Don't say: "Could you delight clean?"
- Do say: "Could y'all do the dishes earlier going to bed?"
Express
- Allow others know how a situation makes you experience by clearly expressing your feelings;
- Don't expect others to read your heed;
- Try using this line: "I feel ___ considering ___."
Affirm
- Don't beat out around the bush—say what you demand to say;
- Don't say: "Oh, well, I don't know if I can cook this evening or not;"
- Do say: "I won't be able to cook because I'm working late."
Reinforce
- Reward people who respond well, and reinforce why your desired issue is positive;
- This can be every bit simple as a smile and a "thanks."
Mindful
- Don't forget the objective of the interaction;
- Information technology can be easy to get sidetracked into harmful arguments and lose focus.
Appear
- Appear confident;
- Consider your posture, tone, middle contact, and torso language.
Negotiate
- No one can have everything they want out of their interactions all the fourth dimension;
- Be open to negotiation;
- Do say: "If you wash the dishes, I'll put them away."
Under the Human relationship Effectiveness (Give) skills department, the handout lists the following:
Gentle
- Don't attack, threaten, or express judgment during your interactions;
- Accept the occasional "no" for your requests.
Interested
- Testify interest by listening to the other person without interrupting.
Validate
- Be outwardly validating to the other person'due south thoughts and feelings;
- Acknowledge their feelings, recognize when your requests are demanding, and respect their opinions.
Piece of cake
- Take an piece of cake attitude;
- Try to smiling and act lighthearted.
Finally, these skills are listed under the Self-Respect Effectiveness (FAST) section:
Off-white
- Be fair; not merely to others but also to yourself.
Apologies
- Don't apologize unless information technology's warranted;
- Don't apologize for making a request, having an opinion, or disagreeing.
Stick to Values
- Don't compromise your values just to be liked or to get what you desire;
- Stand upwards for what you believe in.
True
- Avoid dishonesty such as exaggeration, acting helpless (as a form of manipulation), or outright lying.
It may be helpful to refer to this handout when y'all are faced with a situation in which you struggle to stick to your standards.
The quick reminder and helpful suggestions tin make sure you lot get dorsum on the correct track.
Exploring Action Tendencies Worksheet
This worksheet can assistance you lot raise your client'southward awareness of action tendencies that stem from their emotions – both positive and negative.
The activity helps you guide your client through two main steps, and a debrief for each.
Use Function One, a guided meditation, to help your client identify how they respond to their emotions. Briefly, you volition:
- Invite them to shut their eyes, recalling a recent time where they struggled with a tough emotion. 1 example might be a disagreement with a loved one;
- Encourage them to pic the difficult situation and relive it as much as possible. Where were they? Who were they with?
- Ask them to take notation of the strongest emotion or feeling that arose from the state of affairs, locating information technology if possible in their torso. They volition ideally exist able to label it.
- Assistance them in exploring their instinctive responses to the emotion. What practise they experience like doing now? Annotation that this is not near how they reacted at the time, but what want to do in the moment equally they revisit this experience.
Part 2 takes your customer through a similar guided meditation, but this time they will explore activeness tendencies that are related to a positive emotion instead. This allows you and your client to compare and contrast the 2 – how were they different? What did they notice about each?
This Exploring Action Tendencies exercise can help your client connect the dots betwixt a galvanizing event and the reaction they had to the effect. Among other things, information technology can exist particularly useful for clients who would similar to target their impulsive tendencies or urges.
Skills for Regulating Emotions
This is another corking handout for reminding yourself of the tools at your disposal to help y'all in regulating your emotions.
The handout lists four skills that you tin can apply to meliorate your emotion regulation and provides suggestions on implementing these skills.
Contrary Action
The first skill is Contrary Action, which tin can help you stop an intense or highly charged emotion in its tracks.
Emotions often come up with a specific beliefs, similar arguments post-obit anger, or withdrawal resulting from sadness. However, we often assume the relationship is from the emotion to behavior, rather than the other mode around.
Actually, information technology is possible to invoke an emotion by engaging in a behavior that is associated with that particular emotion.
Instead of doing what you would commonly do when y'all are feeling a certain way, try doing the reverse action. If y'all're aroused, try talking quietly instead of yelling. If you lot are sorry, effort chatting with friends instead of withdrawing from them.
Check the Facts
It tin be easy to blow things out of proportion or place too much importance on your emotions.
This skill will help yous to identify this scenario correct when it's happening, and then aid you reduce the intensity of the emotions.
Ask yourself the following questions to "check the facts":
- What event triggered my emotion?
- What interpretations or assumptions am I making about the event?
- Does my emotion and its intensity match the facts of the state of affairs? Or does it merely match my assumptions of the situation?
P.50.E.A.S.E.
The P.LE.A.S.Eastward. skill is another skill that acknowledges the link between body and brain. You will likely notice it much easier to manage your emotions if you lot likewise manage your health and your trunk.
Remember to:
- PL – Treat Concrete Illness;
- E – Eat Healthily;
- A – Avoid Mood-Altering Drugs;
- S – Sleep Well;
- E – Exercise.
Follow these suggestions to keep your torso healthy and happy, which makes information technology easier to keep your mind happy and healthy.
Pay Attention to Positive Events
Humans are surprisingly good at filtering out the positive and focusing on the negative. Information technology's natural, merely it'southward not helpful!
If you notice you are paying also much attention to the negative, suspension and refocus onto the positive. Y'all tin practice by doing i modest, positive activity every twenty-four hour period, focusing on the adept parts of the activity equally you do information technology. Ignore small problems and notice the enjoyment, pleasure, and fun!
Some small, positive activities include:
Positive Activities Include an Unrushed Repast. Prototype by Maggie Morrill from Pixaby.
- Have a practiced, unrushed meal;
- Lookout a movie;
- Visit with friends or family;
- Visit a local attraction like a zoo or museum;
- Get for a walk;
- Put on headphones and do naught but listen to music;
- Have a picnic;
- Give yourself a relaxing night in;
- Try a new hobby.
This handout can be found online hither.
Emotion Regulation Pictures
 These fun and engaging pictures are all-time suited for children and adolescents, just there's no rule that adults can't do good from them too.
These fun and engaging pictures are all-time suited for children and adolescents, just there's no rule that adults can't do good from them too.
What Zone am I in?
This epitome uses familiar and like shooting fish in a barrel to understand traffic signs to aid the reader easily recognize his or her emotion, place the "zone" they are in, and recall about how to motion to the green zone from any of the other zones.
The like shooting fish in a barrel-to-place symbols make understanding the zones simple for children, and intuitive for anyone who has paid attending to the earth outside of their machine!
The Remainder Area/Blueish Zone is where the private is to the lowest degree energetic or purposeful and includes these emotions:
- Sad;
- Tired;
- Ill;
- Bored.
The Go/Green Zone (the place you want to be!) is the happy medium and represents positive emotions and a rest between extremes. These emotions fall into the Go/Greenish Zone:
- Calm;
- Set up to acquire;
- Happy;
- Okay.
In the Slow/Yellow Zone, things are getting a flake troubling. Emotions include:
- Silly or wiggly;
- Frustrated;
- Hyper;
- Upset.
Finally, the Stop/Ruby Zone is the virtually problematic, with emotions and behaviors like:
- Mad;
- Angry;
- Yelling;
- Hit.
Once the child has identified their emotion and figured out which zone they are in, there is a handy list of suggestions to help them get into, or stay in, the Become/Dark-green Zone, including:
- Drinkable water;
- Count to 10;
- Take deep breaths;
- Tense and release;
- Do wall pushups;
- Use fidgets;
- Depict;
- Write;
- Talk to an adult;
- Ask to take a break;
- Self-talk;
- Enquire to take a walk;
- Volcano breaths;
- Do stretches;
- Listen to music;
- Lift something heavy;
- Ask to eat a snack;
- Think of a at-home place.
This paradigm included below is an excellent addition to whatever classroom, daycare, or other location where immature children are probable to be.
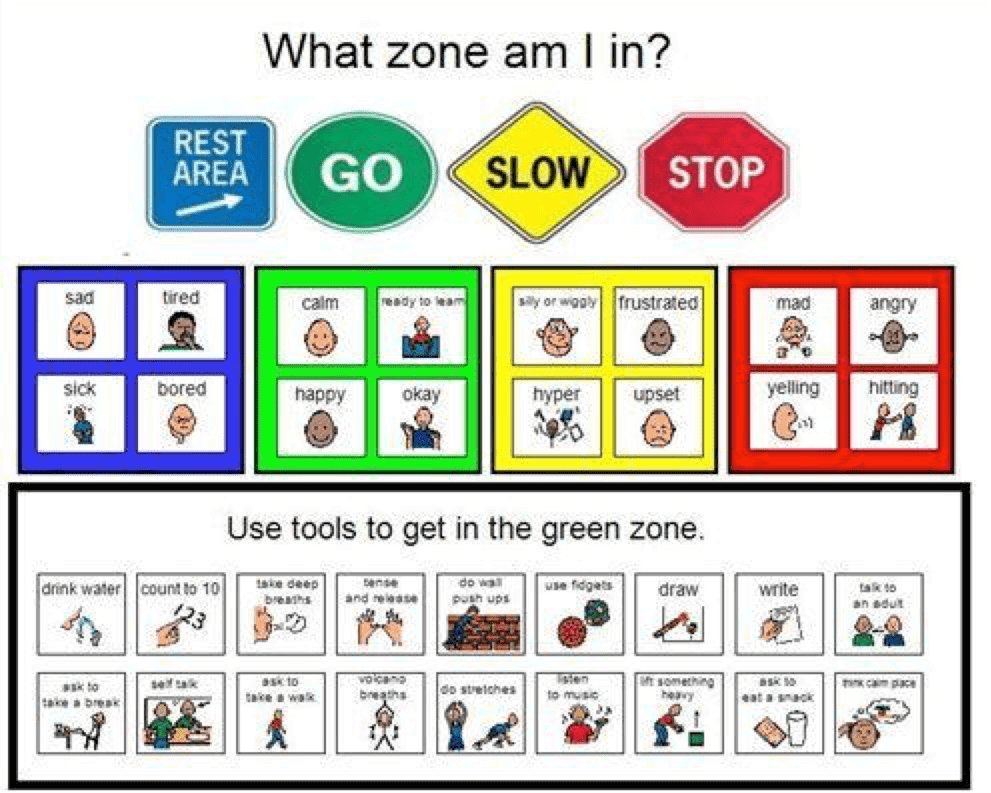
(Image from Pinterest)
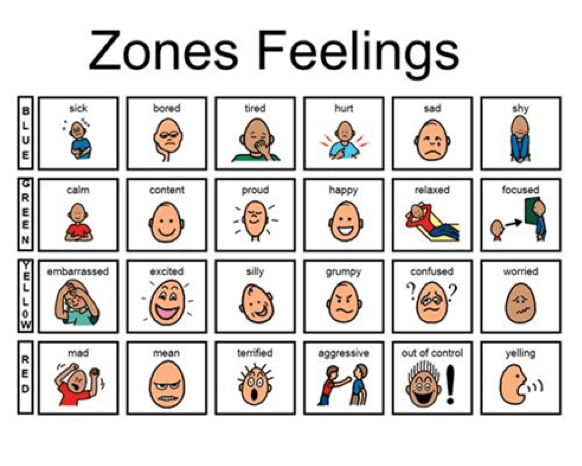
This bonus paradigm adds some more feelings to each zone, including:
- Injure and shy to the Rest Expanse/Blueish Zone;
- Proud, relaxed, and focused to the Become/Dark-green Zone;
- Embarrassed, excited, grumpy, dislocated, and worried to the Slow/Xanthous Zone;
- Mean, terrified, aggressive, and out of control to the Stop/Red Zone.
How Are You Feeling?
(Image from http://boardmakeronline.com)
This image is another that would make a great poster for a classroom, especially with a laminate terminate and an erasable marking for drawing expressions at the bottom.
Information technology poses a fairly simple question: How are yous feeling? If the reader is non sure how they are feeling, it can guide the reader in identifying his or her emotion.
Besides the titular "How are y'all feeling?" question, information technology also asks iii follow-upwardly questions:
- What are yous thinking about?
- Exercise you know why you lot feel this fashion?
- What do y'all wish would happen?
Adjacent, it shows and describes 12 different emotions or feelings, including:
- Good or great;
- Okay;
- Friendly;
- Loving;
- Energetic;
- Hopeful;
- Stressed;
- Mad;
- Confused;
- Lonely;
- Sad;
- Shocked;
- Feelings Keep Changing (you feel a lot of dissimilar ways at in one case, or your feelings keep irresolute).
Finally, it leaves room for the reader to describe a new emotion that they would like to feel, and give the emotion a label. This tin be a fun activeness for young children, and it encourages them to call back near their emotions.
How Big is My Problem?
Although this image was developed with children in heed, it can be adapted to be a great guide for people of whatsoever historic period who need help in determining how big their trouble is.
Information technology tin exist all too easy to blow problems out of proportion, or "make mountains out of molehills." If you notice yourself struggling with this a lot, this emotion picture show may be able to help yous.
It lists the 5 levels a trouble tin potentially be on, starting with the most serious and moving towards the least serious.
Level 5: Emergency – Tornado, fire, danger, serious injury
Potential emotions: Enraged, terrified, hysterical, angry
Level 4: Big Trouble – Fighting, getting lost, someone gets injure
Potential emotions: Upset, scared, mad, broken-hearted
Level three: Medium Problem – Minor accident, existence disrespected, feeling sick
Potential emotions: Worried, frustrating, exhausted, hurt
Level 2: Little Trouble – Forgetting homework, lost supplies, can't make up one's mind what to practise
Potential emotions: Unhappy, disappointed, annoyed, embarrassed
Level 1: Glitch – Losing a game, non getting the supply you want, being late
Potential emotions: Okay, content, fine, calm
Use this handy guide to help children (or yourself!) to identify where the problem is, and make up one's mind how to best respond to the situation.
Traffic Low-cal
The final image would be perfect for very young children, as it is based on a concept that is very easy to understand: a traffic lite.
Print an image of a traffic light, and help the small-scale children in your life determine the deviation betwixt "Green" emotions like happiness, contentment, and feeling at peace; "Yellowish" emotions like boredom, irritation, and sadness, and; "Reddish" emotions similar acrimony, grief, and shame.
Explain that we all experience a wide range of emotions, and it's okay to feel nonetheless they feel. All the same, it is all-time for them if they figure out how to keep their emotions within Green and sometimes Xanthous while limiting the time they spend in Red.
Tell them there are many means to do this. This can be an excellent atomic number 82-in for mindfulness practise or any other emotion regulation skill development!
A Take-Home Message
This piece beginning described emotion regulation, then emotion dysregulation, and and so explored the ways in which you can motion towards the former from the latter.
I hope you found this information enlightening and useful, and I promise y'all become some good use out of the resource nerveless here.
Take you ever worked on your emotion regulation skills? What techniques did yous use? Would you use whatsoever of these techniques? Let the states know in the comments section beneath.
Thanks for reading, and encounter yous adjacent time!
We promise you lot enjoyed reading this commodity. Don't forget to download our three Emotional Intelligence Exercises for free.
- Bray, S. (2013). Emotion regulation in Dialectical Behavioral Therapy. Good Therapy. Retrieved from https://www.goodtherapy.org/web log/emotion-regulation-dialectical-behavior-therapy-dbt-0318135.
- Carpenter, R. W., & Trull, T. J. (2013). Components of emotion dysregulation in Borderline Personality Disorder: A review. Current Psychiatry Reports, xv, 335.
- Dietz, L. (2012). DBT skills list. DBT Cocky Assistance. Retrieved from world wide web.dbtselfhelp.com/html/dbt_skills_list.html.
- Garnefski, N., Kraaij, V., & Spinhoven, P. (2001). Negative life events, cognitive emotion regulation, and emotional problems. Personality and Private Differences, xxx, 1311–1327.
- Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for bear upon, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85, 348-362.
- Hofmann, S. G., Carpenter, J. Thousand., & Curtiss, J. (2016). Interpersonal Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (IERQ): Scale development and psychometric characteristics. Cognitve Theory and Research, 40, 341-356.
- www.kidmechanix.com.
- www.pinterest.com.
- Rolston, A., & Lloyd-Richardson, Eastward. (n.d.). What is emotion regulation and how do nosotros do it? Cornell Research Program on Cocky-Injury and Recovery. Retrieved from http://world wide web.selfinjury.bctr.cornell.edu/perch/resources/what-is-emotion-regulationsinfo-cursory.pdf.
- Tartakovsky, M. (2015). 3 DBT skills anybody tin benefit from. Psych Central. Retrieved from https://psychcentral.com/blog/archives/2015/08/28/3-dbt-skills-everyone-tin-benefit-from/.
- www.therapistaid.com.
- Vivyan, C. (2015). STOPP. Become Self Help U.k.. Retrieved from https://world wide web.getselfhelp.co.uk/stopp.htm.
Source: https://positivepsychology.com/emotion-regulation-worksheets-strategies-dbt-skills/
0 Response to "Review of the Dialectical Behavior Therapy Skills Workbook for 13 Year Olds?"
Post a Comment